How to Install Nginx using Ansible Playbook
March 21, 2023

Nginx is a popular open-source web server known for its high performance, reliability, and scalability. Ansible, on the other hand, is a powerful automation tool that enables you to configure and manage infrastructure as code. In this tutorial, we'll guide you through the process of installing Nginx using an Ansible playbook.
Prerequisites
Before we dive into the installation process, you'll need to ensure the following requirements are met:
- A remote host running a supported Linux distribution (such as Ubuntu or CentOS)
- SSH passwordless access to the remote host
- Ansible installed on your local machine
Steps:
Create Ansible Inventory
We'll create an inventory.cfg file that lists all the hosts we would like to manage.
[web]
34.100.185.153 ansible_user=ubuntu
The above inventory file defines a single host under the "web" group. The host's IP address is 34.100.185.153, and Ansible will use the "ubuntu" user to connect to it.
This inventory file can be used by Ansible to run commands or playbooks on the specified host(s).
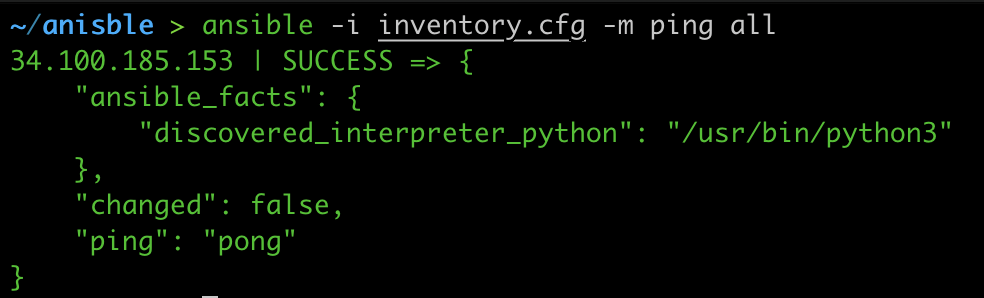
Run the below command to ping all the hosts.
ansible -i inventory.cfg -m ping all
Output:
Create Ansible playbook
We'll create Ansible playbook name install_nginx.yaml to install Nginx server on all hosts mentioned in inventory.cfg under web group.
---
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: install nginx
apt: name=nginx state=latest
- name: start nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: started
The first line, "---", is a YAML syntax marker indicating the start of a YAML file.
The "hosts" line specifies the group of hosts that the playbook will run against, in this case the "web" group.
The "tasks" section lists the individual tasks that will be executed on each host in the group. In this case, there are two tasks.
The first task, "install nginx", uses the "apt" module to install the Nginx web server. The "name" parameter specifies the name of the package to install (in this case, "nginx"), and the "state" parameter specifies that Ansible should ensure the package is installed and up to date.
The second task, "start nginx", uses the "service" module to start the Nginx service. The "name" parameter specifies the name of the service (in this case, "nginx"), and the "state" parameter specifies that Ansible should ensure the service is running.
Overall, this playbook will ensure that the Nginx web server is installed and running on all hosts in the "web" group.
Run Ansible playbook
We have prepared our inventory.cfg and playbook install_nginx.yaml.
Execute the below Ansible command to run the playbook.
ansible-playbook -i inventory.cfg nginx_install.yml -b
ansible-playbookis the Ansible command used to run a playbook.-i inventory.cfgspecifies the inventory file to use. In this case, the inventory file isinventory.cfg.nginx_install.ymlis the name of the playbook file to run. In this case, the playbook file isnginx_install.yml.-bis a short form of the--becomeoption, which tells Ansible to run the playbook with elevated privileges (i.e., as a superuser). This option is typically required for tasks that require elevated permissions, such as installing packages or modifying system configuration files.
So, putting it all together, the command will run the nginx_install.yml playbook against the hosts listed in the inventory.cfg file, with elevated privileges.
Output:
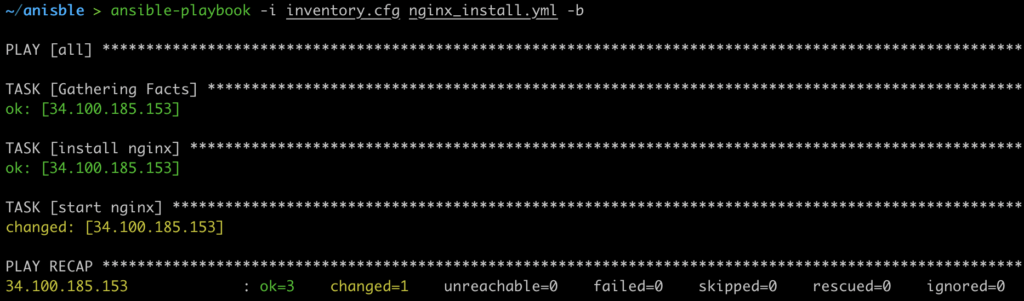
Now we have successfully installed the Nginx server using the Ansible playbook.
Uninstall Nginx using Ansible Playbook
We have learned to install Nginx using Ansible playbook now we'll see how we can uninstall the Nginx using the Ansible playbook.
We'll use our existing inventory.cfg file and to uninstall we'll create a new yaml file name uninstall_nginx.yaml.
---
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: stop nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: stopped
- name: uninstall nginx
apt: name=nginx state=absent
- The
---at the beginning of the playbook is a YAML syntax marker indicating the start of a YAML file. hosts:web specifies that the playbook should apply to all hosts under web in the inventory.- The
taskssection lists the individual tasks to execute on each host. - The first task,
stop nginx, uses theservicemodule to stop the Nginx service. Thenameparameter specifies the name of the service to stop (in this case, "nginx"), and thestateparameter specifies that Ansible should ensure the service is stopped. - The second task,
uninstall nginx, uses theaptmodule to uninstall the Nginx package. Thenameparameter specifies the name of the package to uninstall (in this case, "nginx"), and thestateparameter specifies that Ansible should ensure the package is uninstalled.
Overall, this playbook will stop the Nginx service on all hosts and uninstall the Nginx package from each host.
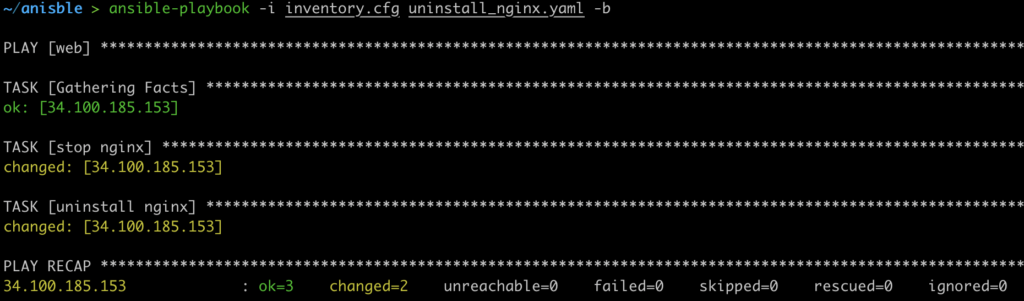
Run the below command to uninstall the nginx
ansible-playbook -i inventory.cfg uninstall_nginx.yaml -b
Output:
Conclusion
Installing Nginx using Ansible is a straightforward and efficient way to manage web servers at scale. Ansible makes it easy to automate the process of installing and configuring Nginx on multiple hosts, ensuring consistency and reliability across your infrastructure. We can also use ansible to configure Nginx by simply copying the Nginx conf file and reloading the nginx to use the new conf. we'll cover the configuration part in next blog.